It’s easy to be inspired by beautiful images, whether they’re your own or someone else’s. If you’d love to take your own photos up a notch but are (understandably) intimidated by mechanical photography jargon such as depth of field, aperture or bokeh, fear not! We’ve put together a helpful glossary of photographic terms to assist with every project, device or technical glitch to help with your move from hobbyist to enthusiast in the field of photography. Whether you’re an amateur, professional, or somewhere in between, it helps to know the technical terms used by professions will absolutely come in handy for those moments of confusion. Find an easy definition for every common photography term from A-Z (or aperture to zoom!). With our photography terms on hand, we can ensure your days in the dark are over and don’t forget to print photo cards to show off those beautiful photographs!
A
A-D Converter
Converts an analog signal that is emitted from the image sensor into a digital signal.
AA Filter
Anti-Aliasing Filter, found on the sensor of a digital camera. Helps eliminate issues that can occur with color aliasing and create a"moiré" effect.
Aberration
A distortion of image quality or color rendition in a photographic image caused by optical limitations of the lens used to capture the image. Commonly found on the edge of photographs, looks like"smearing."
Absolute resolution
Image resolution expressed using horizontal and vertical pixels. Eg. 1600x1200 pixels.
Absorption
When light is absorbed by a surface, its energy is converted to heat through the process of absorption.
Abstract
An image that is created apart from the standard structure of reality, recognizable by its emphasis on line, color and geometrical form.
AC Power
Alternating Current, used as an alternate direct power source in lieu of the battery.
Acquire
To import images into a software program for post-processing. Terminology usually changes depending on program.
Acutance
A measure of the sharpness pertaining to the edge of an object.
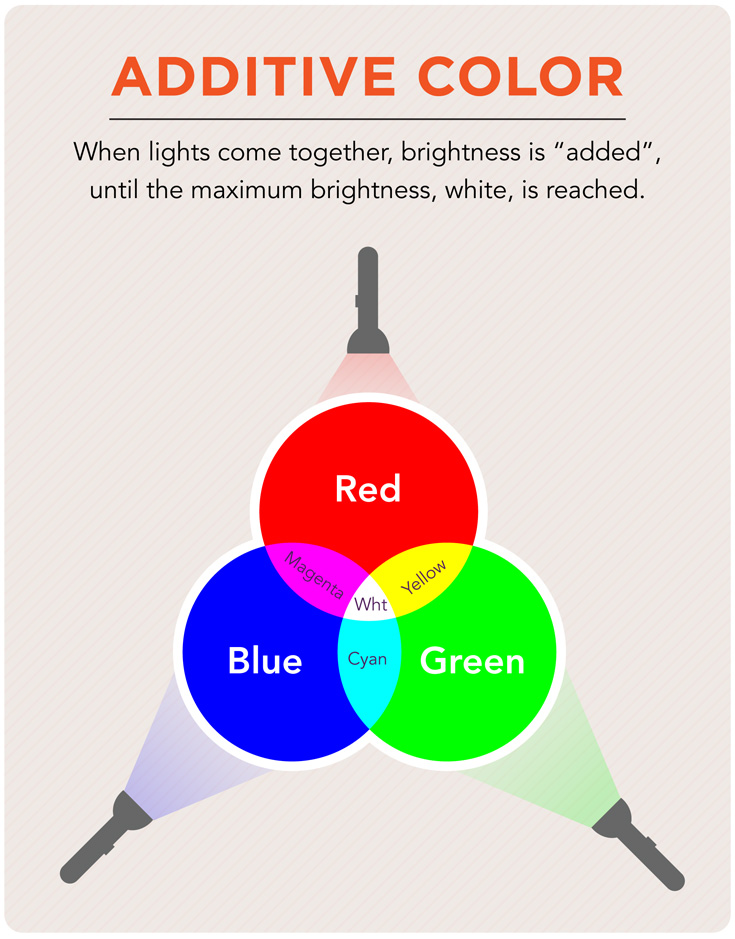
Additive Color
The result of mixing colors of light to create a new color. When Red, Green and Blue lights are mixed together they create pure white light.
Add-on Lens
Low end attachment for lenses or camera phones that normally changes the focal length of the lens. Screws on to lens via the filter thread.
Adobe RGB (Adobe RGB 1998)
A standardized color space that provides a wider range of color than the more common sRGB color space. Adobe RGB is the preferred color space when an image is intended for print.
AE (Auto Exposure)
A camera mode that automatically chooses settings for a particular scene (i.e. shutter speed, aperture and white balance).
AE Lock
Enables you to lock the current exposure reading and re-frame the shot using the same setting. A half-press of the shutter is normally required to activate this function, fully pressing only when you want to capture the image.
AF (Auto Focus)
All digital cameras and most modern SLR lenses have the option of autofocus. The lens automatically focuses on a subject, the difference is that an SLR also has the option to focus manually.
AF Servo (Continuous Focus)
By partially pressing the camera’s shutter release button, AF servo allows the photographer to continuously maintain focus on a subject that is moving within the frame. This allows the shutter to respond faster as the subject is already in focus.
Afocal Projection
When a photograph is captured by attaching a camera to the eyepiece of a telescope, the image result is an afocal projection.
Aliasing
The process by which smooth curves and lines that run diagonally across the screen of a low-resolution digital file take on a jagged look as opposed to looking smooth and natural.
Ambient Light
The existing light in a scene provided by nature, not artificially by the photographer.
Anamorphic Lens
A lens that compresses a wider angle of view into a standard frame. This creates a widescreen image by giving a different magnification of both the horizontal and vertical plane.
Angle of Incidence
The angle at which light strikes a surface and is transformed from"incident" to"reflected" light. The angle at which the reflection occurs is equal and opposite to the angle at which the light struck the surface.
Angle of Reflectance
The angle made by a reflected light ray that is perpendicular to the reflecting surface. See"Angle of Incidence."
Angle of View
The amount of space captured by a lens. The angle of view is determined by the combination of sensor size and focal length.
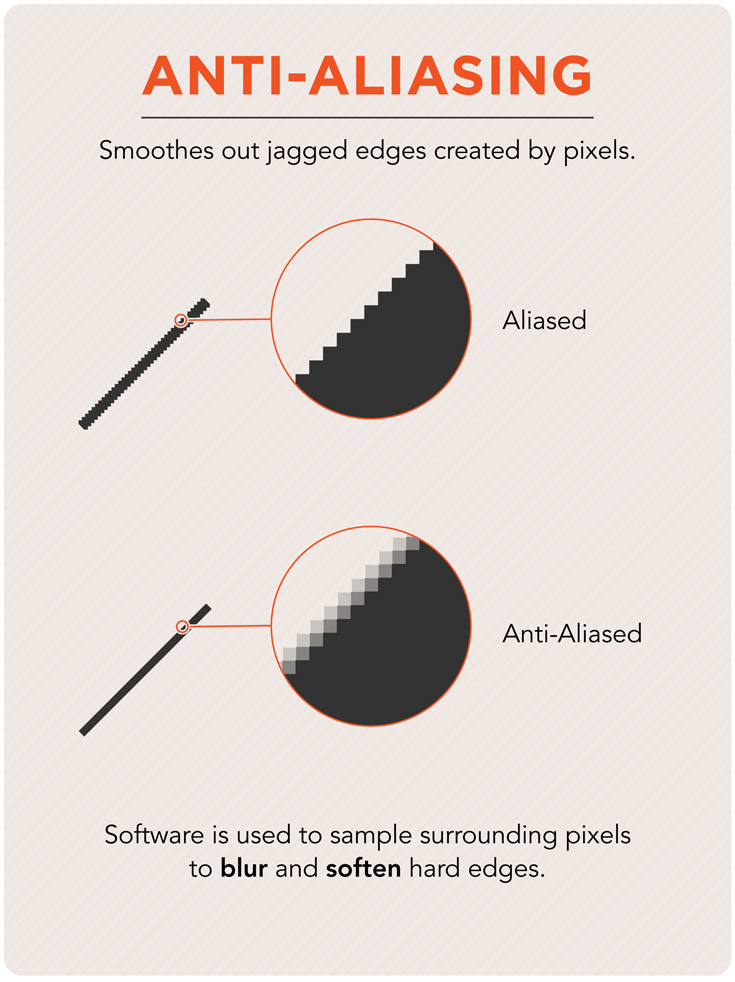
Anti-aliasing
A process by which the edge of an object is smoothed out in a digital image to reduce the"stair-case" effect.
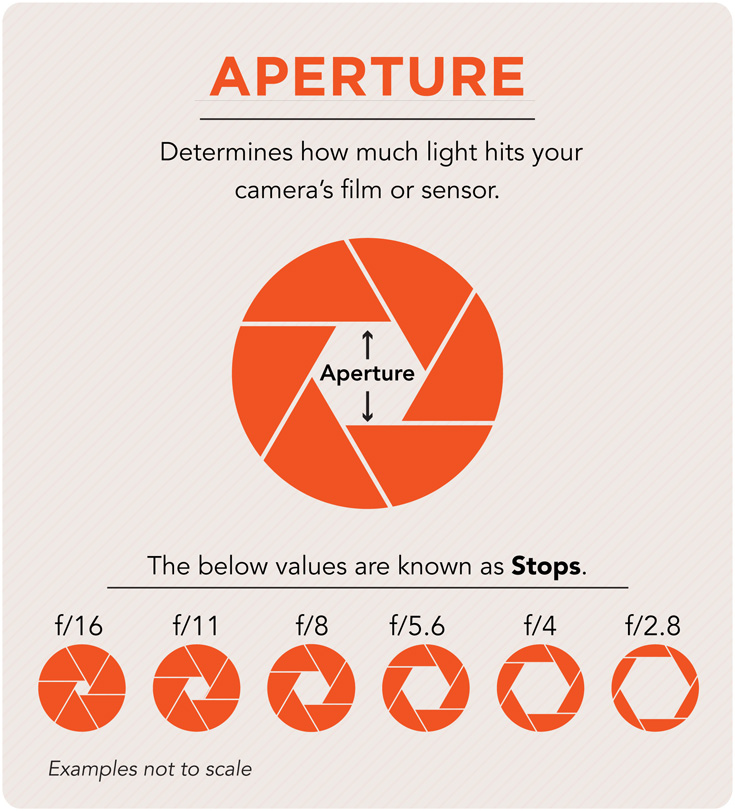
Aperture
The adjustable opening of a lens that determines how much light may pass through the lens."Faster" lenses have wider apertures and allow for faster shutter speeds that stop motion. The wider the aperture is set, the shallower the depth of field of the image.
Aperture Preview
A button or switch on some cameras that permits you to look at the scene with the aperture stopped down to the proper opening intended for the photograph.
Aperture Priority
A metering mode that allows the photographer to set a desired f-stop, thus allowing the camera to automatically set the appropriate shutter speed for the scene.
Apochromatic (APO)
A lens that causes all visible light wavelengths to focus on the sensor or film plane. Any lens without this correction will tend to maintain focus with red, green and blue wavelengths on different planes.
APS-C Sensor
Used to describe the size of the digital imaging sensors in most compact DSLRs. APS format is 50% smaller (23.6 x 15.8mm) than a standard 35mm frame (24 x 36mm) and has a 1.5x magnification factor (multiply the focal length x 1.5) for determining the 35mm equivalent focal length of lenses used on APS-C format cameras.
APS-H Sensor
APS-H format sensors (1.3x) are smaller than a full-frame but maintain a larger frame than that of an APS-C.
Archive
A collection of data in long-term storage, usually the hard drive on your PC or an external hard drive.
Artifact
Artifacts refer to distortions within the image as a result of image compression or interpolation. Artifacts can be seen as light halos around dark areas of an image or as a"blocky" quality in the highlight area of an image. Forms of artifacts include blooming, chromatic aberrations, jaggies, moiré, noise and halation.
Artificial Light
Illumination created by the photographer or that is not naturally present within a scene.
ASA (American Standards Association)
A term used to describe the light-sensitivity levels of film and camera imaging sensors. The higher the number, the more sensitive—or faster—the film or sensor is.
Aspect Ratio
The height and width ratio of the image produced in camera. The aspect ratio of a 35mm image is 3:2 while a computer monitor is mostly made of images containing a 4:3 ratio.
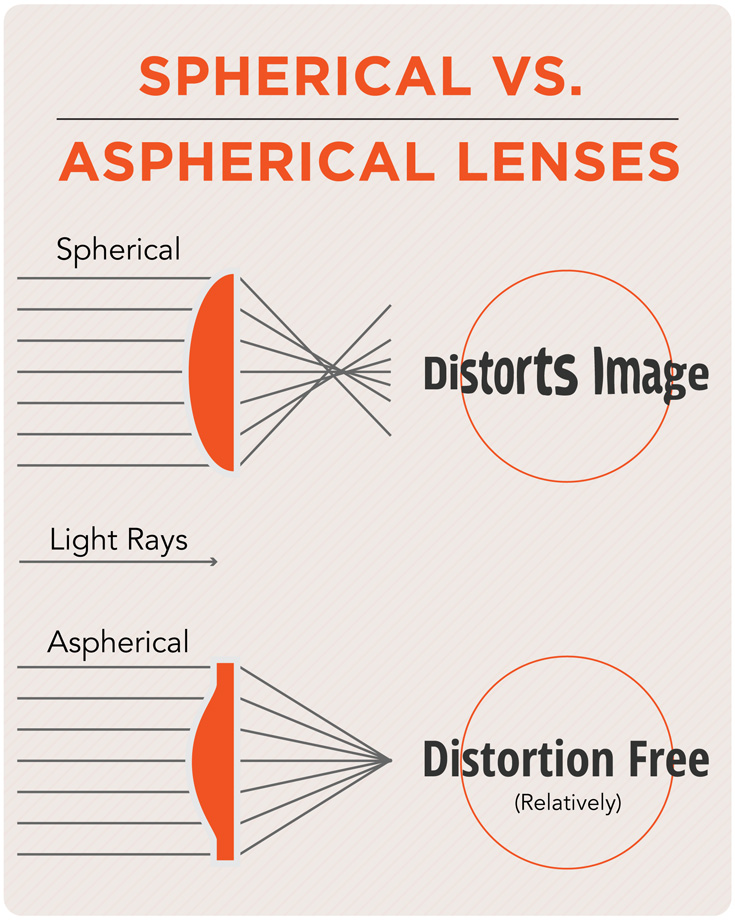
Aspherical Lens
A type of lens that changes shape across its surface as opposed to one that is smooth and continuous. The lens will deviate a little from exactly a spherical shape, and stays predominantly abberation free.
ATGNI
An acronym"All the gear, no idea." A comment about amateur photographers who have no idea what they’re doing, but maintain proper gear.
Audio
Almost all digital cameras can record audio to go alongside their ability to capture video. Depending on the make and model of the camera, sound can be recorded by a variety of tools including an in-camera microphone or specialty audio capturing accessory.
Auto Bracketing
When a camera is set to automatically bracket multiple exposures for multiple images by pressing the shutter a single time.
Autofocus
The ability of the camera and lens to keep the subject in focus during the exposure. Autofocus can be Continuous, meaning focus is maintained regardless of where it moves within the frame, or Single, meaning the point of focus is locked regardless of where the subject may move.
Automatic Aperture
An automatic aperture remains fully open until the shutter is pressed, which then allows the aperture to close to a size predetermined by a light meter within the camera. All point & shoot cameras maintain an automatic aperture.
Automatic Exposure
A camera’s ability to adjust aperture and shutter speed automatically using an internal light meter and achieve optimal exposure.
Auto ISO
A feature that allows the camera to choose optimal ISO depending on the situation. When there is enough light to use ISO 100, the camera will do so, but when there is less light the camera will adjust accordingly to to avoid unintended blur.
Average Metering
A process that measures all of the light values for a scene and averages them together to determine the best overal exposure. Average metering is best used for subjects facing a direct light-source surrounded by otherwise"normal" lighting conditions.
AVI
A file format for movie clips in Windows AVI format. Many digital cameras now come with the option to record in this file format.
AWB (Auto White Balance)
A function by which the camera senses the color temperature provided by ambient light and automatically adjusts color balance to a neutral setting.
B
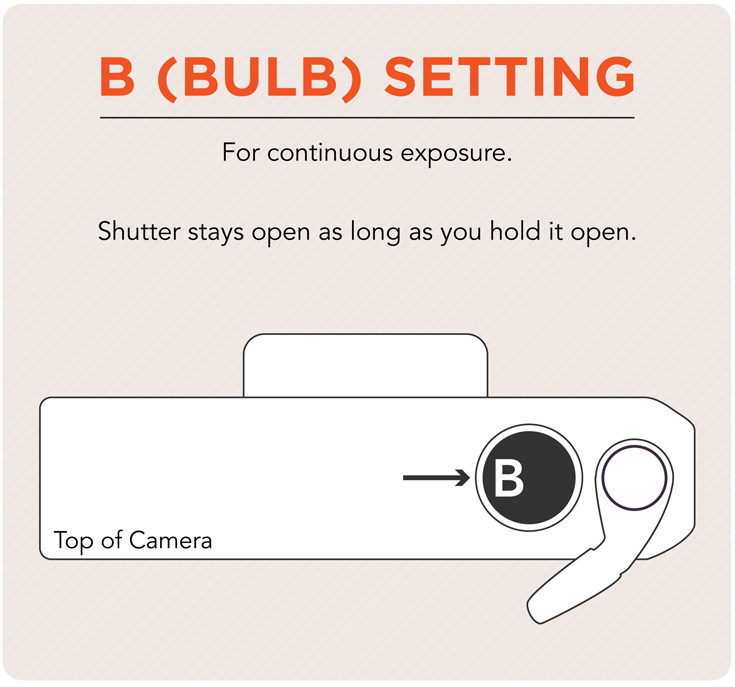
B (Bulb)
A setting on the shutter speed dial which indicates that the shutter will remain open as long as the release button is held. This is often used with a cable release so that the shutter may stay open for extended periods of time.
Back Lit
Meaning the subject is lit from behind which can cause uneven exposure. Also used for portrait photography, special effects and bringing catchlights to hair.
Background
The part of a scene that appears to be the furthest distance from the viewer, and normally behind the subject.
Backlight
The illumination behind a color LCD display on digital cameras. Can also refer to the light behind a subject within a setting.
Backlight Control
An override of the camera’s auto-exposure setting that increases the exposure by between one and two stops. Use this mode to prevent a silhouette when taking photos while the light is behind the subject.
Backscatter
Refers to suspended particles in water that are illuminated by an underwater flash caused them to reflect light and become"circles of confusion."
Back-up
A safety measure that involves copying an image, file, folder or an entire hard drive to be stored in the event that the original files or data is lost. This can also be used as a noun to refer to the hard drive where the data is stored.
Balance
The harmony of a scene. A balanced composition involves cohesive placement of shape, size and color.
Banding
When graduated colors are broken into larger blocks of a single color, the smoothness of the color gradation is reduced.
Bare Bulb
A source of electronic flash that is direct and free of any reflection or diffusion.

Barn Doors
A light-blocking device that attaches to studio lights and swivel on hinges to allow the photographer to control both the direction and width of the light source.
Barrel Distortion
An optical distortion in which the image bows out of square, to make the shape of a barrel. Barrel distortion is usually the product of an inexpensive wide-angle lense or fisheye lense on a digital camera. It can be seen in photographs of architecture where lines run parallel to each other on both the horizontal and vertical planes.
Batch Edit
Editing a large quanity of photos at one time. This is done by applying the same edits and style to multiple photos from a single folder.
Batch Scan
The process of scanning more than one image at once. This is only recommended if the tonal value of all images are equal.
Bit (Binary Digit)
The smallest unit of digital information, eight bits is equal to one byte. An image can be described by the number of bits representing a single pixel. The more bits available, the greater range of color the image will have (i.e. 1-bit = monochrome; 8 bit= 256 colors or grayscale; 24 & 32 bit = even greater range).
Bit Depth
The number of bits used to represent a single pixel in a digital image.
Bitmap
A method of storing digital information that maps out an image one bit at a time. Pixel density is used to describe how sharp the resolution of an image will be.
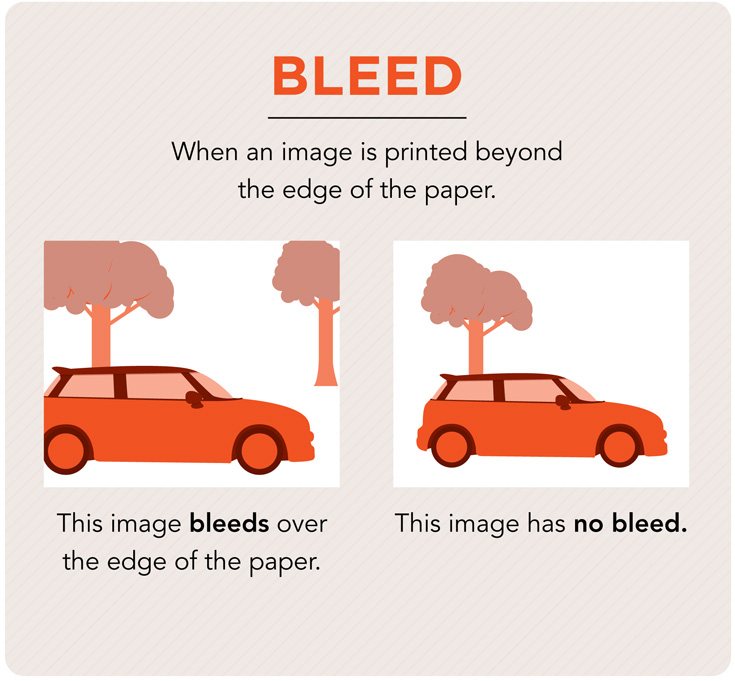
Bleed
The edges of a piece of paper by which photographic print has no visible border or defined margin area.
Blocked Shadows
The loss of shadow detail within an image. An image that has been underexposed or contains a lower resolution will often cause this result.
Blooming
A bright or colored halo seen in brighter areas of a digital image. This effect can be caused when the camera’s sensor is exposed to too much light.
Blow Up
Another term for a print or photographic enlargement, usually considered to be anything larger than 8"x10".
Blown out
An effect caused by overexposure, and results in a complete loss of the highlight details in a photograph.
Blur
Denotes movement within a photograph that is either caused by the subject or by camera movement. Blur can also be added to digital files in post processing with image-editing software.
BMP
The file extension for an uncompressed image file. It is mainly used in Windows-based applications.
Bokeh
A japanese translation that refers to a"haze" or"blur" found within an image. Pronounced boh-keh, it is the out-of-focus area in a photograph that is created by a shallow depth of field.
Borderless
A photograph printed without the border or white"stroke" often found around the edge of an image.
Bounce Flash
Light that is reflected off of a surface before it reaches the subject. Reflectors, ceilings and bounce cards are often used as surfaces for reflection.
Bracketing
Taking multiple images of the same scene at different exposures. Increments in exposure often range from 1/3 stop to a full stop.
Brightness
The value of a pixel in a digital image in reference to lightness. A black pixel is represented as"0" while a white pixel is represented as"256."
Broad Lighting
When the main light illuminates the camera side of a subject’s face.
Buffer Memory
An area where image data is waiting to be processed by the camera. A camera may continue to capture new images, rather than shut down, while the image files wait in the buffer.
Built-In Light Meter
An in-camera exposure meter that measures the light reflected in the present scene.
Burning
In the darkroom, it refers to providing extra exposure to a specific part of the print to darken that area while blocking the rest of the print from light. Digitally, this term refers to a tool in Photoshop that performs the same action by applying a brush that darkens specific parts of an image.
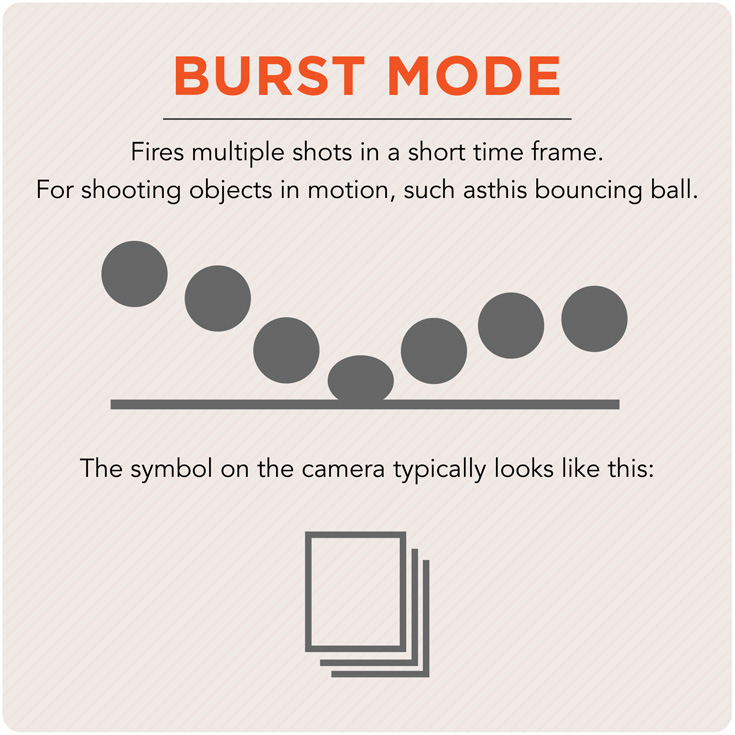
Burst Mode
A mode on the camera that allows for taking continuous photos with a single press of the shutter release. Many of today’s SLRs reach 14 frames per second.
Burst Rate
The total number of images a digital camera can capture in Burst Mode.
Butterfly Lighting
When the main light is placed high and directly center above a subject’s face casting a butterfly-like shadow.
Byte
A collection of 8-bits of memory in a computer.
C
C-41
The standard photochemical process for developing color negative film.
CC Filter (Color Compensating Filter)
Enables the photographer to make detailed adjustments in color tone or density when practicing color photography.
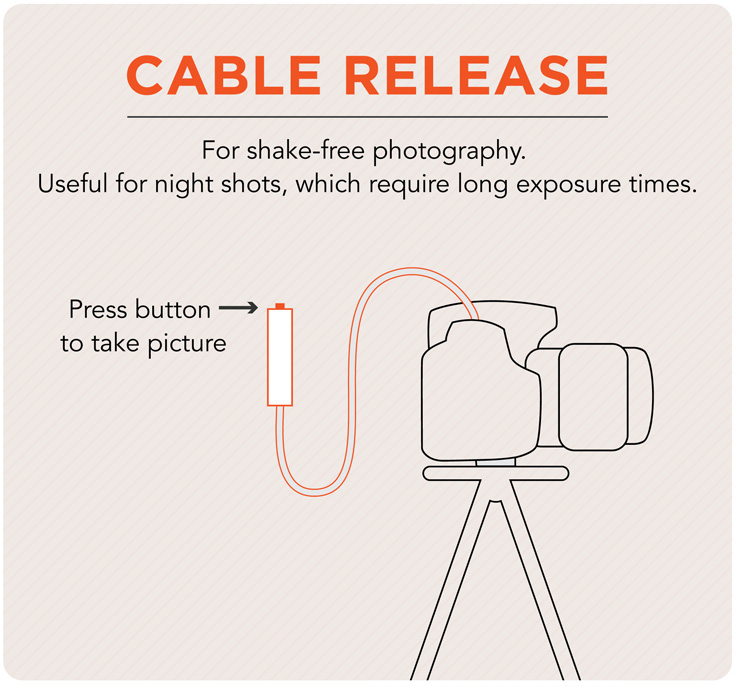
Cable Release
A cable with a push-button that sends the camera a signal to open the shutter. The shutter then stays open as long as the cable release button is depressed. This is used predominantly in night time photography allowing cameras to capture more light.
Calculator Dial
The adjustable scale on an electronic flash. The dial will determine an appropriate aperture for the flash-to-subject distance once the photographer has set the film speed or chosen an ISO setting.
Candid
A photo taken without the (apparent) knowledge of the subject.
Capacity
The amount of storage space available on a hard-drive or media card.
Card Reader
A digital memory card reader is used to transfer data from a media card to a computer drive.
Catchlight
The reflection of light that can be seen in the eyes of a subject.
CCD (Charge-Coupled Device)
A device that converts an optical image into electronic signals. CCDs contain rows and columns of ultra small, light-sensitive mechanisms (pixels) that, when electronically charged and exposed to light, generate electronic pulses that work in conjunction with millions of surrounding pixels to collectively produce a photographic image. CCDs and CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) sensors are the dominant technologies for digital imaging.
CD (Compact Disc)
A method of storing and transferring data from one place to another.
Center-Weighted
A type of metering mode in which the light reflected in the center of the frame is measured to give the most influence on the proper exposure for a photograph.
CF (Compact Flash)
Used to record images in a digital camera. Capacity can range from multiple megabytes to hundreds of gigabytes.
Channel
A single piece of color information stored with an image. True color comes in 3 channels, red, green and blue.
Chimping
Looking at pictures on the back of the camera as soon as they’ve been taken, often accompanied by oohs and aahs.
Chroma
The color of an image element or pixel. The hue values of the pixel, plus the saturation determines the chroma.
Chromatic Aberration
Referred to as color fringing, this effect occurs when all wavelengths of color fail to focus on the same focal plane. Chromatic abberation can be seen at the edges of an image with high contrast.
CIFF (Camera Image File Format)
A type of raw image format design for DSLR cameras.
Circle of Confusion
Discs of light formed by the lens, due to points of light being within the area of bokeh when photographing a scene.
Clipping
A result of over/under exposing a photo so much that there is loss of information in the highlights or shadows of the histogram.
CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)
A type of Imaging Sensor used to capture light and convert it into electrical signals. Previously considered inferior to CCD sensors, CMOS sensors have vastly improved and are now the dominant sensor technology because they are less expensive to manufacture and consume less energy.
CMY
Three secondary colors that can be combined to create any other color in the spectrum. CMY is used in printing and has less dense blacks than CMYK.
CMYK Color (Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black)
A color space that is used for professional or commercial printing. CMYK is the standard color space used for inkjet, laser, dye-sublimation and wax thermal printers.

Codec
An application used in playback that encodes or decodes video, allowing it to play. A codec must be used or you will not be able to record or play video.
Color Balance
The manner in which film reproduces a scene under different types of lighting. Also, a tool in Photoshop used to adjust color by manipulating RGB channels.
Color Break
The meeting place of two colors in an image. Where one color"breaks" and the other begins.
Color Calibration
A process by which the image source (camera) and image output (monitor) are calibrated to ensure the same color standard. This ensures that the color of images viewed on a camera will match the colors seen on a monitor, and therefore match the colors seen on a print.
Color Cast
An unwanted tint of a specific color that is"cast" across the image. It can be corrected with image editing software.
Color Correction
Altering the colors in an image in order to print or display it as intended. This is normally performed by utilizing post-processing programs programs such as Lightroom or Photoshop.
Color Depth
The amount of unique colors represented in a specific image or software. May also be referred to as bit depth.
Color Management
A system for coordinating the calibration of color spaces within digital cameras, scanners, monitors and printers to ensure that the image on the screen has the same values as the image in print.
Color Palette
The set of colors available for a specific image. Computers often have a color space that contains up to 16 million different colors, but image editing requires that a color space be chosen for the image, normally this range is up to 256 colors.
Color Space
The range of colors produced on a computer screen or in print. The most common color spaces include sRGB and the wider-gamut Adobe RGB (1998).
Color Temperature
The light spectrum specifically defined through color temperature. The spectrum is measured by degrees of Kelvin (K). The lower the color temperature the"cooler" a photo will be, and the higher it is the"warmer" it will be.
Colorimeter
A device designed to analyze the color characteristics of a specific swatch, or set of colors.
Complementary Color
When a primary or secondary color is in opposition to each other on a color wheel (ex. red and green are complementary colors). When dealing with light in terms of photography, complementary colors include blue & yellow, green & magenta and red & cyan.

Composition
The specific arrangement or combination of elements within a scene.
Composite Photographs
A single image made by combining pictures from different sources into one.
Compression
Reducing the size of an image file through image editing software."Lossy" images will lose detail after compression while"Lossless" images will maintain all the qualities of the image.
Conflicting Shadows
Shadows that point in the direction of each other as well as main light in a studio lighting set-up.
Contact Sheet
A contact print made from several negatives or RAW files at one time, usually an entire roll or whatever number of frames will fit on the paper.

Continuous Autofocus
A mode set so that the auto focus system is continuously keeping the subject sharp and in focus through multiple frames.
Contrast
The range of difference between highlights and shadow areas in an image. Contrast can be natural (direct vs. diffuse light) or adjusted in a variety of image editing programs.
Crop Factor
A number used to multiply a lens’ actual focal length to express how much of an apparent increase you can expect in the effective focal length of any traditional 35mm SLR lens you use on a DSLR with a crop sensor. Standard crop sensors are 1.3x, 1.5x or 1.8x the normal focal length of a lens.
Cropping
Trimming the edges of an image to improve compisitional quality. The final image is a reduced size of the original composition, image editing programs have cropping as a tool.
CRW
The RAW CCD file format used by Canon Digital Cameras. Comes from Canon RAW.
Cyc Wall
A curved, normally seamless wall that is used as a backdrop for studio photography.
D
Dark Current (aka"Noise")
When a pixel does not collect enough light, it collects a signal charge in its absence. This creates the appearance of noise which is similar to"grain" on film. Mostly noticeable in the shadow areas of images captured at higher ISO ratings.
Darkroom
A room that is completely dark, with no light allowed into the room. The purpose of this room is for light-sensitive materials such as film to be handled without fear of their exposure to light.
DC (Direct Current)
Battery power, such as a 9v DC battery.
Decompression
Large data files often need to be compressed into a smaller sized files. Decompression is the act of reversing this compression.
Dedicated Flash
An electronic flash that automatically reads the camera’s exposure values allowing for full automatic use of the flash. This means that the flash will read the scene, the camera’s settings and then flash the appropriate power.
Definition
Image sharpness as defined by clarity of detail.
Density
How opaque or purely black an area of a negative, transparency or print is. The darker or more black the image is, the less light will be allowed to travel through it.
Depth of Field
The the distance of the area of focus from the foreground of the subject to the background. The smaller the aperture is, the longer the distance will be. Conversely, a wide aperture will minimize the distance of the depth of field.
Depth of Field Scale
A scale on the lens barrel with the markings of f/stops and distances, which shows the distance range that is in focus for a chosen f/stop.
Depth of Focus
Depth of focus is the measurement of the area in focus within an image, from the closest point of focus to the furthest point of focus.
Diaphragm
A ring or plate with a hole in the center, this is what controls the size of the aperture. The larger the hole, the more light will be let into the sensor and vice versa.
Diffraction
A redistribution of light’s energy when passing through the edge of an opague object.
Diffused Light
Light that is scattered and spread out as opposed to direct light. Diffused light is softer than direct light, with shadows that are less sharply-defined. A good example would be an overcast day where the sun is completely blocked by clouds.

Digital Asset Management (DAM)
The process of managing tasks and making conclusions regarding the import, export, annotation, cataloguing, storage, retrieval and distribution of digital assets such as image files.
Digital Film
The process of capturing motion pictures as digital video images, as opposed to the historical use of motion picture film.
Digital Negative (DNG)
An open raw image format used by image editing software. It is similar to a TIFF and allows for metadata storage.
Digital Zoom
When a digital camera zooms in on a image for cropping it on the sensor. This is the opposite of optical zoom and creates lower resolution image files.
Dioptre Adjustment
A knob used to adjust the clarity in the viewfinder of a camera. This feature adjusts for the discrpenacy in human eyesight.
Distortion
The misrepresentation of the size of proporition of the subject within a scene. This can be due to the use of a wide angle or fish eye lens.
Dithering
Creating the illusion of new colors and shades by varying the pattern of dots. Dithering can be found in newspapers and is also known as halftoning.
Dodging
Lightening a portion of the image using a tool in Photoshop or by blocking the light during the exposure of a print.

Doughnuts
The name given to the ring-shaped bokeh produced by a mirror lens.
Download
The transference of image data from a camera to a computer. Can be performed through USB, Firmware or wirelessly.
DPI
A term when describing the resolution quality of an image. PPI (Pixels per Inch) is used when describing monitor resolution. The higher the PPI/DPI, the higher the resolution of an image will be. For magnifying images up to life size on a computer screen, 72 DPI is required. For offset printing the image must be set to 300 DPI to print at a desired size, and for inkjet prints, DPI must be between 180 and 360 at the desired print size.
DPOF (Digital Print Order Format)
Allows for printing information to be embedded on an image file.
DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
A type of volatile memory, which is lost when the power is turned off.
DRAM Buffer
The amount of capacity the buffer memory holds for a camera. DSLRs can hold up to 32MB in order to store multiple images at a time.
DSLR (Digital Single Lens Reflex)
A single lens reflex camera that captures digital images.
Dust Bunnies
Dots of sensor dust that show up on images in the exact same place. SLRs have interchangeable lenses will allow for the sensor to be exposed to air during switching, giving dust the opportunity to get in.
DVD (Digital Versatile Disk)
Method of information storage often used for large files. May be recorded on a DVD-R or DVD-RW disc.
Dye Sublimation
A printing method involving waxy ink and high temperature that give a continuous tone color to images. The word sublimation is used because the dye goes straight from being a solid to a gas and completely skips the liquid stage.
Dynamic Range
The range of brightness and tonality reproduced in a digital image. Wider dynamic range translates into greater tonal values (and detail) between all tones in the image.
E
E-TTL (Evaluative Through The Lens)
An exposure system that calculates exposure by briefly flashing before the image is taken.
Effective Pixels
Refers to the area of pixels that the sensor can cover, which usually equates to about 99.9% of the frame. The 0.1% left refers to the edges of the image and to providing color information for the image.
Electronic Viewfinder (EVF)
A digital replication of the field of view captured by the lens. This can be found on the back of most modern DSLRs.
Equivalent Exposures
By choosing an ISO speed, the light meter will yield settings for both the aperture and shutter speed. Equivalant exposures can be achieved by adjusting the shutter speed and aperture in equal increments.

Enlarger
A light projection device used to project an enlarged image through a lens onto photographic paper. A film negative is placed between the lens and the paper allowing for only specific areas of light to reach the paper.
EV (Exposure Value)
The ability to override the auto exposure system to under or overexpose the image. This is done by using the Manual function on a digital camera to choose your own settings.
EVIL (Electronic Viewfinder Interchangeable Lens)
An acroynm used to describe the CSC (Compact System Camera).
EXIF (Exchangeable Image File)
Commonly used header format for storing metadata (e.g. camera/lens/exposure information, time/date/, etc.) within digital image files.
Export
The process of sending a file out of one application and into another. The term is also used to describe the action of saving the data to a specialized file format (i.e. JPEG or GIF).
Exposure
Exposure occurs when light strikes the surface of film or a digital sensor. Exposure is determined by the volume of light passing through the lens. The proper exposure for a given scene can be accomplished a variety of ways.
Exposure Bracketing
The process of taking a photo, then also taking photos at both a higher and lower exposure value. This technique is used to ensure quality by having a multitude of exposures to choose from.
Exposure Compensation
Either overexposing or underexposing from the suggested exposure from the camera’s light meter.
Exposure Indicator
A display showing the amount by which a photograph recorded at the current aperture and shutter speed will deviate from the suggested exposure selected by the camera.
F
F-Stop (Aperture)
A term used to describe the aperture. Common f-stops include 1.8, 2, 2.8, 4, 5.6, 8, 11, 16, and 22.
Falloff
A decrease in the intensity of light as it spreads out from the source.
Fast Lens
A lens with an aperture that opens particularly wide, making it able to gather more light than a slower lens at its widest aperture. Examples of fast lenses include f/2.8 or wider.
Field Monitor
Highly accurate alternative to the LCDs found on the back of digital cameras. Field monitors allow for a more precise look at the field of view.
File
A collection of information like data, text or images which can be located on a CD, DVD or hard drive.
File Format
The type of file an image is saved as to a digital memory card. JPEG, TIFF and RAW are the most commonly found file formats for digital cameras.
Fill in Flash
Flash that fills in a darker area with a certain amount of light. Fill flash is not intended to overpower the main light, but bring out the detail lost in shadows.
Fill Light
The light itself that produces a fill flash. See"Fill in Flash."
Filter
A clear piece of glass, plastic, or gelatin that is appened onto a lens to affect how an image looks.
Filter Thread
Most SLR cameras have a threaded ring at the front end of the lens. The diameter of the lens’ filter thread is measured in millimeters.
Filter Size
Refers to the inner diameter of the front of the lens, more specifically the threads into which a filter is screwed to attach it to the lens.
FireWire
A computer connection wire used for high speed data transfer.

Firmware
Software programs for digital cameras that have Read-Only Memory (ROM). This controls the interface from which the photographer operates the camera.
Fisheye
Describes an extreme wide-angle lens that has an angle of view exceeding 100 - sometimes more than 180 - and that renders a scene as highly distorted.
Fixed Aperture
Aperture that remains constant regardless of the lens’ focal length.
Fixed Focal Length Lens
A lens that does not have a zoom feature (ex. 50mm, 85mm, 100mm, etc). These are normally faster lenses because they possess the ability to have a wider aperture.
Flare
When light strikes the inside of the lens, a reflection can be seen in the image alongside a reduction in contrast and visible light shooting from its source.
Flash
A brief, sudden burst of bright light or the unit used to create artificial light.
Flash Memory
This is the equivalent of film for digital cameras, except it is a reusable memory source with an infinitely larger capacity for memory.
Flash Meter
An exposure meter designed to measure light from an electronic flash.
Flash Sync
The fastest shutter speed a camera can"sync" with its electronic flash. When the camera is at too high of a shutter, only parts of the image will receive light causing large rectangles of pure black in the photo.
Flash Exposure Compensation
A feature that allows the photographer to add exposure compensation to the flash output power. Flash Exposure Compensation can be + (plus) or - (minus) in increments of 1/3 EV (Exposure values).

Flat
A term used to indicate an image has low contrast (i.e. a"flat" image).
Flat Lighting
Illumination of a scene or subject that provides little contrast on the subject or scene. Flat light can be seen on cloudy days and in front of softboxes.
Focal Length
The distance between the focal point of a lens and the film plane. This refers to the relative size of the lens (i.e 24mm, 50mm, 85mm).
Focal Length Magnifier
An indication of the angle of view of a lens scene on a DSLR when it is magnified by a cropped image sensor.
Focal Point
The center of focus in an image. The focus normally refers to the subject or primary part of the photograph.
Focus
A point at which converging rays of light meet after being refracted or reflected. An"in focus" image is something that is sharp and well defined.
Focus Assist
Cameras with this send out a light, either normal or infra red to light up the subject to assist with the autofocus in low light or darkness.
Focus Lock
A feature on a digitalcamera that allows the photographer to stay focused on an object, allowing for all objects at the same distance to be photographed.
Focusing Screen
An element between the mirror and pentaprism in a single-lens-reflex camera. The mirror reflects the image from the lens upward onto the screen. The areas of the image that are in focus are sharply defined on the screen, while the areas that are out of focus appear blurred. The photographer views the image passing through the screen in the viewfinder window.
Follow Focus
A focus-control mechanism used in filmmaking and television production. Follow-focus units have now been applied to DSLRs that shoot video.
Foreground
The area of a scene that is closer than the subject.
Format
The shape and size of film - normally used in reference to small, medium and large format films and the photography equipment employed in handling each different film format.
Four Thirds (4/3)
A compact digital camera format designed around a 17.3 x 13mm imaging sensor, which has half the size of full-frame (35mm) imaging sensors. The sensors in Four Third and Micro Four Third are identical, but they have dissimilar lens mounts.
Frame
Refers to the boundaries or sides within which an image or the viewfinder has been contained.
Frame Rate
Number of frames shown in a second of video. Live action is around 30 frames per second.
Frames Per Second
Frames per second (fps) refers to the number of pictures that a camera is able to take in a second. A point-and-shoot camera typically shoots one or two pictures per second. Higher-end single lens reflex (SLR) cameras have much greater performance, as many as 14 or more frames per second.
Fringing
A common problem with less expensive lenses involves the"bleeding" of color along the edges of contrasty images. Fringing often shows up blurring from cyan, yellow and magenta.
Full Bleed
Otherwise known as"Borderless" printing. Infers that the ink limit extends to all 4 edges of a print.
Full Frame Sensor
A full-frame DSLR digital camera that has a sensor the same size as a frame of traditional 35mm film.
G
Gain
A relationship between the input and output signals of any electronic system. High levels of gain amplify the signal causing more contrast and brightness. Lower levels of gain darken the image and soften contrast. Adjusting gain affects sensitivity to light in a digital camera.
Gamma
The brightness curve of a color spectrum that is displayed on either a computer monitor, a printer or scanner.
Gamma Correction
Controls the overall brightness of an image due to adjustment in its sensitivity to light. Improper gamma correction can look either too dark or bleached out.
Gamut
The range of colors available in an image. Gamut usually describes printer capabilities in reproducing colors accurately and vibrantly.
Gels
Any colored translucent material that is used to color a light. Materials are usually made from gelatin, glass or plastic.

Geotagging
The practice of recording GPS coordinates captured of the place where a photograph was captured.
Gigabyte (GB)
A measure of file space consisting of one billion bytes (a thousand megabytes). The actual value is 1,073,741,824 bytes (1024 megabytes).
Glass
A nickname for lenses, often used by professional photographers once they realize the quality of a lens is more important than the quality of a camera.
Glossy Print
A shiny-surfaced print of an image.
GIF
Graphic Interface designed for using images online. This is a 256-color or 8-bit image.
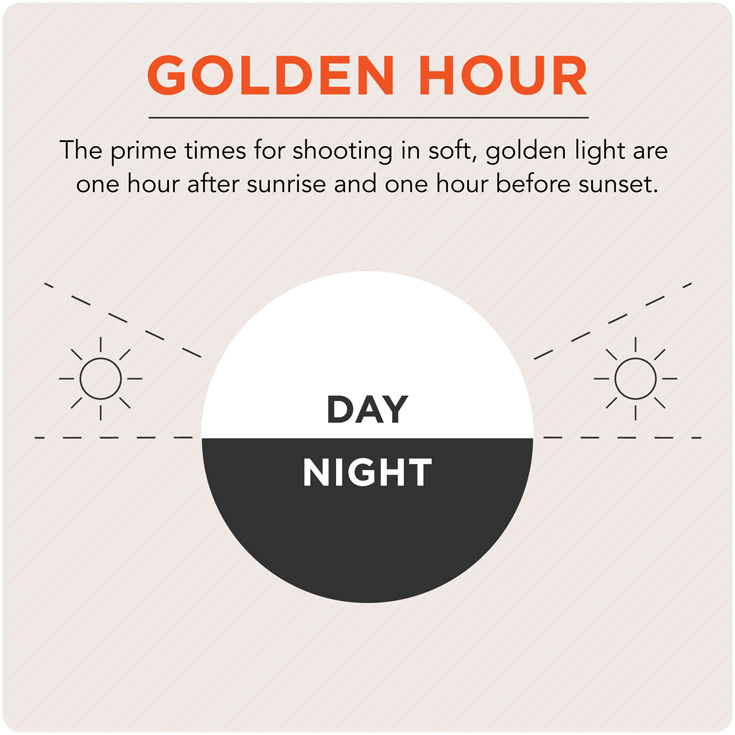
Golden Hour
The time an hour or less before the sun goes down and around fifteen minutes after the sun has set. The sun produces a beautiful effect on the skin as well as a glowing flat light.
GPS (Global Positioning System)
A satellite-based navigation system used for establishing a fixed location. Useful for geotagging images to show where they were taken.
Grad
An abbreviation of ’Graduated’ that is used to describe a type of filter that fades from dark to clear.
Gradation
A smooth transition between a tonal range. Can include transition from black to white, one color to another or color to no color.
Gray Card
A card that is uniformly gray on one side. The gray side reflects precisely 18% of the white light that strikes it. It is used to calibrate a light meter and determine a scene’s optimal exposure value.
Gray Level
The brightness level of a pixel determining its lightness from white to black. Represented as a value from 0 to 255, 0 equaling black, 255 equaling white.
Gray Scale
An image containing purely shades of gray. Also know as a black and white photograph.
Grip and rip / Spray and pray
Setting the camera to its highest continuous drive mode and holding the shutter down with the hopes of catching the image stopped in action and in focus.
GUI (Graphical User Interface)
Pronounced"GOO-ey." A program interface that assimilates the computer’s graphics capabilities and makes the program easier to use.
Guide Number
A flash guide number indicates how powerful a flash is and how large the area it can illuminate.
H
Halftone
A reproduction of an image through a special screen made up of different sized dots. Used to simulate a continuous tone image.
Halos
The glow that’s created around the edges of objects when they have too much clarity or sharpness.
Handgrip
A part of the camera body shaped to be gripped with a hand. In some cameras, it may also provide extra space for batteries to be housed.
Hardware Calibration
Calibrating a digital camera, scanner, printer or monitor using specialized hardware.
HD (Hard Drive)
A large-capacity storage unit for memory that can be housed in an external casing or home computer.
HDR
A technique that enables a photographer to capture a wider range of normal exposure in all areas of a scene. This is done by taking the same photo at different exposures and combining them in an image editing program.
HDSLR
A digital single lens reflex camera (DSLR) that has the ability to capture HD video.
HDTV (High Definition Televeion)
Video standard that has an aspect ratio is 16:9 versus 4:3 of older TVs.
Headshot
Photograph of a person’s head and shoulders. Can be used promotionally for professionals as well as for government documents and identification.
High Key
An image that is predominantly made up of lighter tones, and has relatively few mid-tones or shadows.
Highlight
The specific bright area or range of bright areas within a photograph.
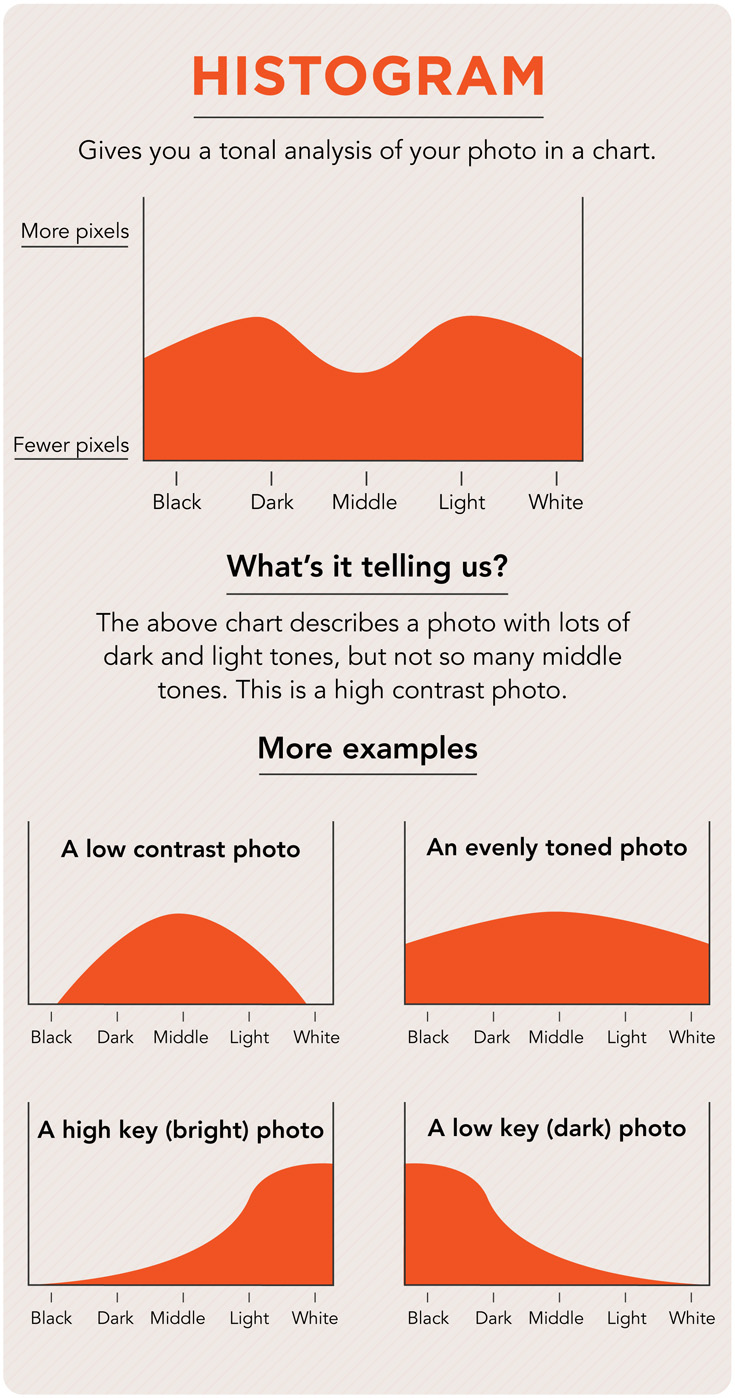
Histogram
A visual representation of the exposure values of a digital image. The visuals include a range in peaks that express the value of tones ranging from highlights to shadows.
Hot Shoe
An accessory"shoe" located on the top of the camera housing that enables the photographer to mount and trigger an electronic flash or wireless transmitter. Hot shoes can also be used for a multitude of other accessories.
Hue
The attribute of a color within the color wheel (Red, Green, Blue etc).
I
ICC Profile (International Color Consortium profile)
A color-management standard that specifies the color attributes of digital imaging devices in order to maintain accuracy and consistency in different mediums.
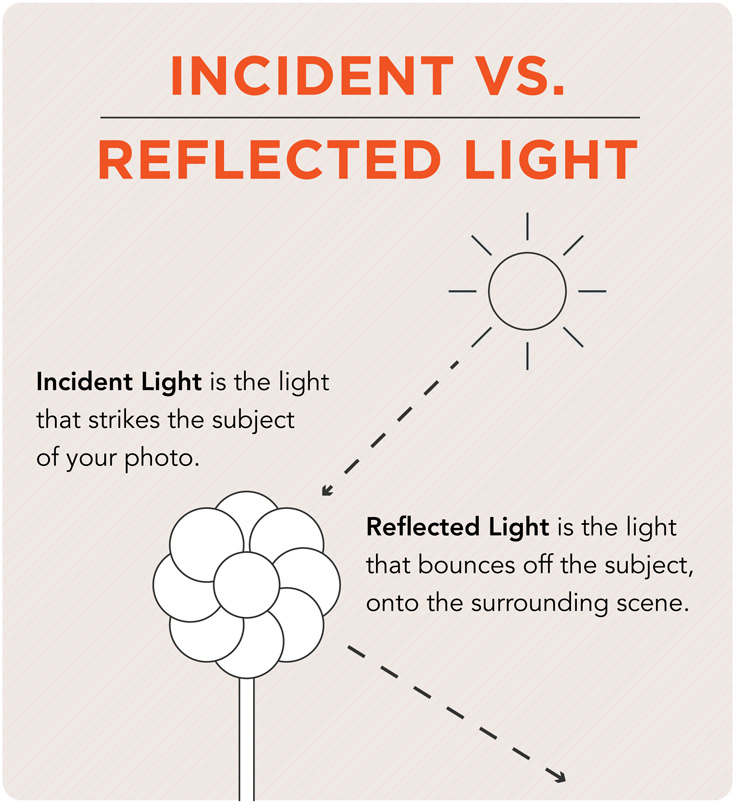
Incident Light
Light falling on a surface - not the light reflected from it. Incident light rays are those that strike an object.
IEEE-1284
High-speed, bidirectional parallel port specification for Windows computers, used to connect printers.
IEEE-1394
See"FireWire."
Image Resolution
Number of pixels in the length of image (ie. pixels per inch, pixels per millimeter, or pixels wide, etc).
Image Sensor
Records the scene being photographed similar to a traditional camera. Unlike film, the image sensor sends the image to a memory card.
Image Stabilization (IS)
A method of reducing the effects of camera movement. It can be achieved either in the lens or the camera body.
Incandesent
Illumination produced from typical household bulbs (tungsten bulbs). The light produced has a yellow-white balance with temperature ranging from 2500K to 3200K.
Infinity
The beginning of the farthest distance of which the lens can focus.
Inkjet
Printing method that involves the spraying micro-jets of ionized ink on a sheet of paper in droplet sizes.
Interchangeable Lens
A removable lens, typically found on SLR cameras.
Interlaced
This is the term used to describe an image sensor that gathers its data by first processing the odd lines, and then processing the even lines.
Interlaced Scan
Video capture technique that entails imagery consisting of two fields of data that are captured a frame apart and played back in a way that reproduces motion naturally and flicker-free.
Interpolated
Most software programs can enlarge image resolution beyond the actual resolution by adding extra pixels. This normally decreases the quality of the image but can be enhanced by a program or plug-in.
Intervalometer
A tool used for time-lapse photography that allows a photographer to capture images at preset intervals.
Initializing
The preparation of the contents of a memory card to enable digital image data recording. Also known as"formatting."
Inverse Square Law
An equation that relates the intensity of a light source to the illumination it produces at a given distance. Light diminishes over distance in accordance with the Inverse square law, which states that doubling the flash-to-subject distance reduces the light falling on the subject to one-quarter.

Image Browser
An application that enables you to view digital photos. Some browsers also allow you to rename files, convert photos from one file format to another and add text descriptions.
Image Editor
A computer program that enables you to adjust a photo to improve or change its appearance.
Image Quality (IQ)
A characteristic of an image that measures the perceived image degradation (typically, compared to an ideal or perfect image). Factors that affect quality include brightness and evenness of illumination, contrast, resolution, geometry, color fidelity and color discrimination of an observed image.
IR (Infra-Red)
A beam of light that is invisible to humans. Is used to either control a device without wires as well as in camera auto focusing systems.
ISO (International Standards Organization)
Film speed rating expressed as a number indicating an image sensor’s (or film’s) sensitivity to light. The higher the ISO, the more sensitive the sensor is to light and the larger presence grain within the image.
J
Jaggies
Nickname for the smooth edges of lines that experience the"stair-step" effect in a low resolution photo.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
The standard image file for digital cameras. JPEG is a"lossy"’ compression format and results in pixelation at low resolutions.
JPG
The file extension for JPEG.
Juxtaposition
When two things are seen or placed close together with contrasting effect.
K
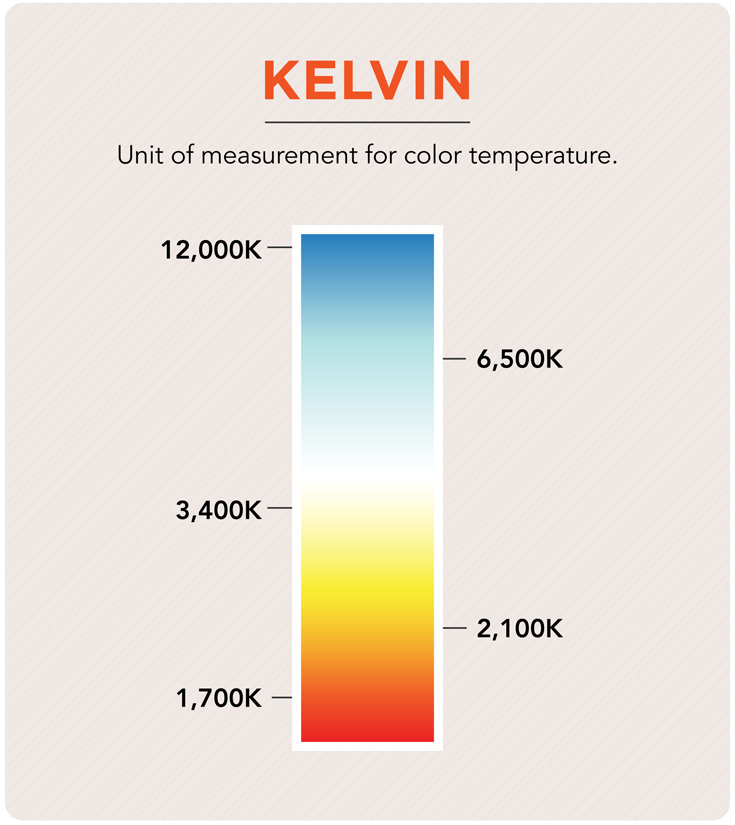
Kelvin
The measurement of degrees when referring to color temperature.
Key Light
The principal source of light in a scene with artificial light. The key light is generally the brightest and has the most overall affect on the subject.
Keystoning
A type of distortion that occurs when a projected image (from a projector) is not directed perpendicular to the screen.
Kicker
A side or back light often near lens height used to rim faces and model profile shots. Used to provide an additional highlight or accent to the subject.
Kilobyte (KB)
1,024 bytes.
L
LAB Color
A linear color space that employs luminance as a means of increasing contrast and color saturation.
Lag Time
The delay that occurs between the time the shutter button is pressed and the image is captured. The less expensive the camera, the more prevalent the shutter lag.
Landscape
A picture of the land and its surrounding natural features from a single viewpoint. Scenery is the subject of a landscape image.
Large Format
A film format that holds individual frames of film that are 4" X 5" or larger.
Latent Image
An invisible image that is recorded on film and must be made visible by development.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
Found on the rear of digital cameras and allows the photographer to preview or review photographers as well as control various aspects of the camera.
Leading Lines
Lines that direct the viewer’s attention to an image’s center of interest or a specific location within a photograph.

LED (Light Emitting Diode)
The small red, green and yellow indicator lights used on most cameras, power supplies and electronic devices.
Lens
A single piece of glass combined with one or more curved surfaces used to change the convergence of light rays. A camera lens is the vehicle by which the image sensor sees an image.
Lens Coating
A coating that reduces light reflection and increases transmitted light.
Lens Flare
The light scattered in lens systems through generally unwanted image formation mechanisms, such as internal reflection and scattering from material inhomogeneities in the lens. These mechanisms differ from the intended image formation mechanism that depends on refraction of the image rays.
Lens Hood
An accessory that attaches like a collar to the front of a lens and prevents light from striking the surface of the lens.
Lithium-ion
A type of rechargeable battery prevalent in digital cameras and camcorders.
Light bucket
A nickname for a fast lens.
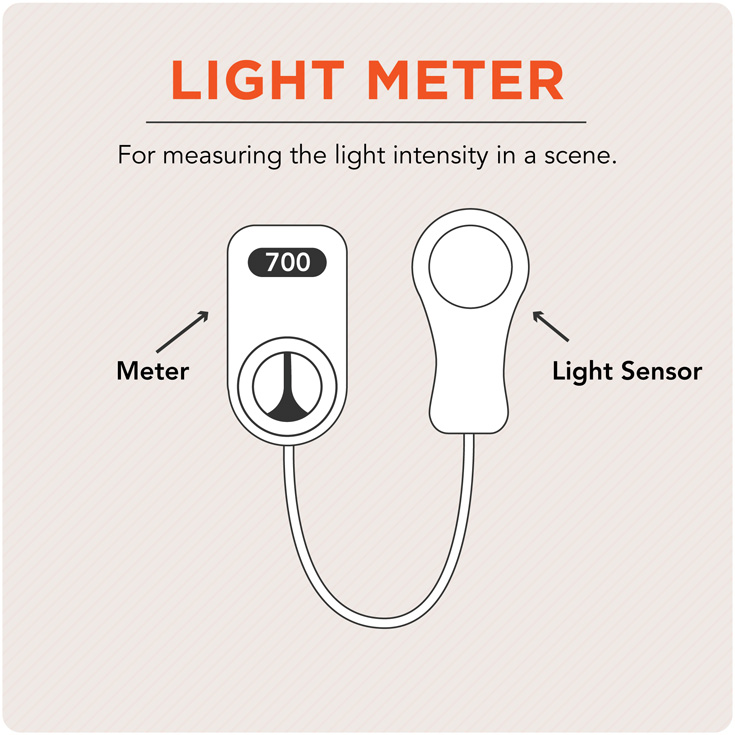
Light Meter
A device used to measure available light and determine the proper exposure for a given scene. The reading tells the photographer which shutter speed and aperture settings to apply.
Light Tent
A tent-like structure made of translucent fabric that diffuses the light coming from outside the tent so that a highly reflective object placed inside the tent can be photographed without seeing any reflections.
Light Trail
A line resulting from movement of a point of light (or camera movement) during a long exposure. Star trails are one example.
Live View
The photographer can see what the lens is seeing, but on the camera’s LCD instead of the viewfinder. The term is not exactly live but gives the effect that it is.
Lossless
A compression technique which lessens file size but allows the image to retain all of its data making them identical in appearance.
Lossy
Data-compression that reduces the detail of a digital image file. An example would be JPEG.
Low Key
Describes an image with mostly dark values and few highlights.
Low Pass Filter
A filter used in digital imaging to suppress color ghosting alongside the effects of infrared light.
Luminance
The intensity or brightness released from a light source.
M
Machine gunner
A photographer who takes more shots than need to. Machine gunners shoot on continuos and have many duplicates.
Macrophotography
Close-up photography where the subject is captured at the same or larger than actual size.
Macro Lens
A lens with the ability to focus extremely close on small objects.
mAh
A term of measurement in reference to power of an electronic device such as an LCD.
Manual Focus
A feature of a camera lens where the user can control the focus adjust by hand.
Manual Mode
A camera mode that allows the photographer to over-ride automatic exposure settings and determine shutter speed and aperture themselves.
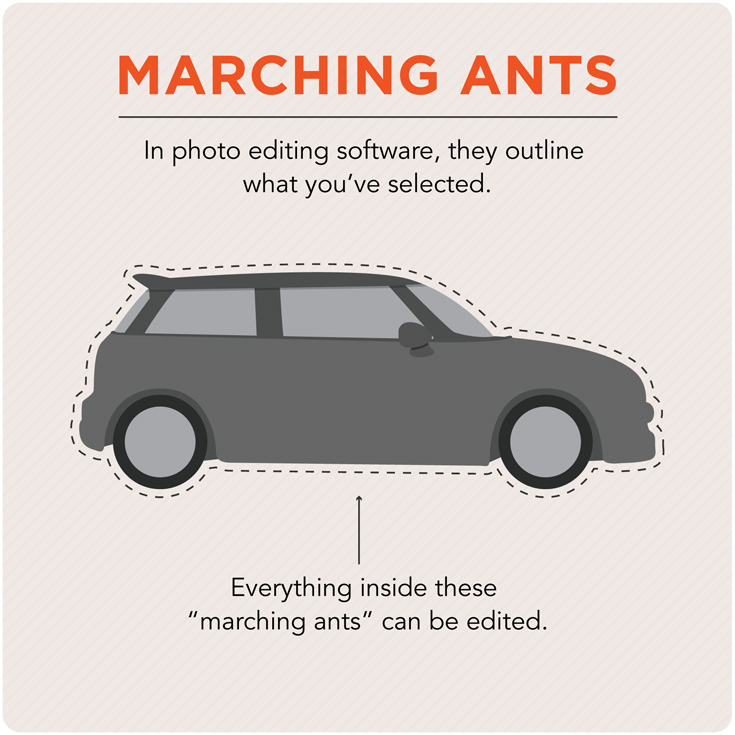
Marching ants
The dotted lines that flicker around areas that have been selected in Photoshop.
Mask
When using image editing software, a mask is a way of protecting specific areas of the image, just as you would use masking tape when painting your house. This is used to adjust specific parts of the image while keeping the rest of the photo unaffected.
Matrix Metering
Takes the total image area and breaks it into sections, then analyzes light in each section and determines proper exposure for the lighting situation.
Maximum Aperture
The widest opening in aperture a lens can afford, such as 1.4 or 1.2.
MB (Megabyte)
1,024 Kilobytes.
MD (Minidisk)
Digital memory storage similar to a small floppy disc.
Medium Format
A type of film that is larger than 35mm, but smaller than 4"x5" large format. Typical medium format film would be a"120 roll" which equates to 6x6 cm when developed into negatives.
Megapixel
When the CCD (or CMOS) resolution is equal to one million pixels.
Memory
The camera’s file-storage medium. Digital cameras employ flash memory, which doesn’t need power to maintain storage once it is saved.
Memory Card
A removable storage device used in digital cameras to store captured images. There are several different types of memory cards available including Compact Flash, SmartMedia, SD/SDHC/SDXC, XD and Memory Stick.
Memory Stick
A flash memory card type from Sony that resembles a stick of chewing gum and varies in size.
Metering
Metering is used to calculate the exposure from the existing light conditions. Includes Matrix Metering, Spot metering and Center-weighted metering.
Mic (Microphone)
Digital cameras that can record audio have a built-in microphone. Some digital cameras also feature an external mic input port, which allow for the use of dedicated microphones during video recording.
Micro Drive
One of the original types of digital memory cards for digital cameras. Essentially a small hard drive, it lost popularity to more reliable flash memory.
Micro Lenses
Micro lenses are normally mounted on top of the light-gathering portion of pixels. They can be angled along the edges of a camera sensor in order to capture and redirect light back into the pixel. This is used to reduce falloff on the edge of photographs.
Midtone
The area of an image or a scene that displays average or"middle" tonal values.
Minimum Aperture
The smallest opening a lens affords. An extremely sharp image with a small aperture would be f/64.
MMC (MultiMedia Card)
A memory card used in some digital cameras that is similar in size and shape to a SD card.
Modeling Light
A tungsten light built into a studio flash that remains on when the flash is in standby mode, allowing the photographer to attain focus prior to the flash going off.
Moiré
A confusion between the photographic scene and the pattern of which the pixels are made up on the sensor.Moiré can often be eliminated either by increasing or decreasing the distance from the subject.
Monochrome
A single-color image. A black and white or sepia-toned image is considered to be monochrome.
Monopod
A one-legged support for a camera, designed similarly to a tripod. Often used as support when shooting events that require a large lens to"stop action" such as sporting events or concerts.

Motion JPEG
A video clip composed of a sequence of JPEG compressed images.
MOV
Apple QuickTime Movie file format.
Movie clip
A motion sequence captured in AVI, MOV or MPEG formats. Many digital cameras have the ability capture short movie clips and can also record sound.
Movie Mode
Camera mode that captures movies or video.
MPEG
Motion JPEG movie file.
Multi-Zone Focusing
The camera automatically determines which zone or area within the scene (center, left, right, upper or lower) is appropriate for performing auto focus.
Multi-Pattern Metering
Measures many different zones in the frame to give an optimum exposure evaluation.
Multi-Point Focusing
An autofocus system that uses several different points of the image to determine the correct focus.

Multiple Exposure
When more than one exposure is exposed on the same frame. Called a"Double-exposure" when two exposures appear together in a single frame.
N
Narrow Lighting
Occurs when the main light completely illuminates only the side of the subject’s face that is turned away from the camera. This can also be called"short lighting."

Natural Light
See"Ambient Light."
Neutral Density Filter
A filter used in front of the lens that absorbs all visible wavelengths and significantly reduces the amount of light that reaches the sensor.
NiCad ( Nickel Cadmium )
A type of rechargeable battery, the NiCad battery was one of the first successful rechargeable batteries used in digital cameras.
Nifty fifty
A 50mm lens with a maximum aperture of f/1.8 or faster. Lenses in this range are fast, lightweight. The"nifty" feature is the price. The f/1.8 and f/1.4 50mm lenses are often the best value for glass you can buy.
NiMH ( Nickel-Metal Hydride)
A commonly used rechargeable battery for digital cameras. A NiMH battery can have two to three times the capacity of an equivalent size nickel-cadmium battery.
Nodal Point
The optical center of the lens.
Noise
See"Dark Current."

Noise Reduction
A process within a digital camera’s image processor that suppresses or eliminates grain within an image.
Non-Volatile Memory
Typically used for the task of secondary storage, or long-term persistent storage. The most widely used form of primary storage today is a volatile form of random access memory (RAM), meaning that when the system is shut down, anything contained in RAM is lost.
Normal Lens
Lens with a focal length approximately equal to the diagonal of the film format or of a digital camera’s image sensor. A scene viewed through a normal lens appears to have the same perspective as the way your eye sees it. Most 35mm cameras normal lenses have a focal length of approximately 50 mm.
NTSC
The 60 field video output (television) standard used in the U.S. and Japan.
O
Objective
An optical system containing a combination of lenses that converge light rays from an object and form an image on the focal plane. A photographic lens is an objective.
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode)
An advanced form of LED that does not require backlighting, the OLED displays more dense blacks and higher contrast compared to standard LEDs.
OOF (Out of Focus)
An acronym that refers to a soft photo.
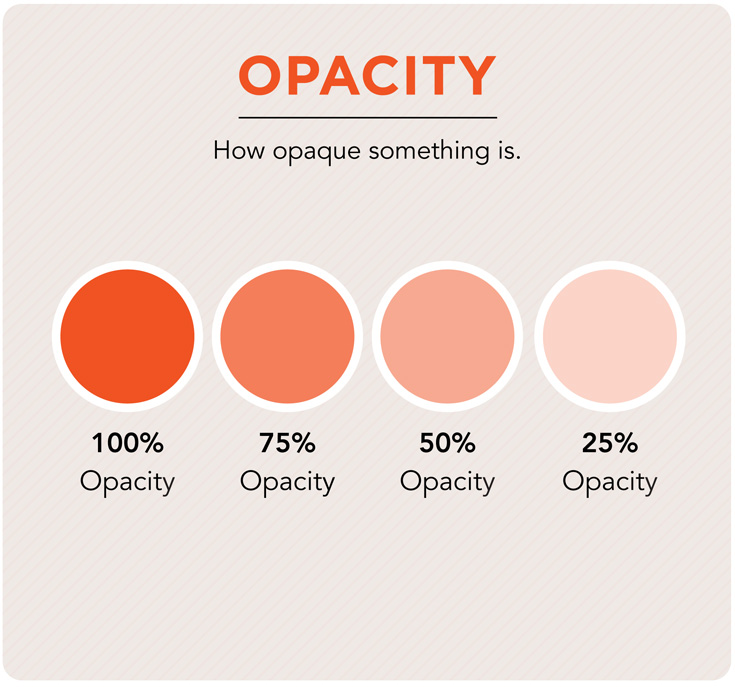
Opacity
The state or quality of being opaque. This term is used in the darkroom when describing the density of a negative. Digitally, it can refer to the density of a layer when working in Photoshop.
Open Up
To increase aperture size or reduction in shutter speed and permit more light to reach the film or image sensor.
Optical Resolution
The physical resolution at which a device can capture an image. The term is used most frequently in reference to optical scanners and digital cameras.
Optical Viewfinder
A viewfinder that is used to compose the photograph.
Optical Zoom
A lens that enables you to change the magnification ratio by either pushing, pulling or rotating the lens barrel. Optical zoom lenses’ focus remains undisturbed when changing focal lengths.
ORF (Olympus RAW Format)
The un-processed image format created by Olympus.
Orientation Sensor
A sensor in a digital camera that can tell when the photographer turns the camera to portrait orientation to take a vertical shot. This is registered for auto-rotation when viewing images in playback.
Overexposure
The result of recording too much light when taking a picture, resulting in a light image.
P
Painting with Light
Occurs when a photographer takes a normally dark scene and incrementally lights it using a handheld light source such as a flashlight. The result is usually created over a long exposure and creates the effect that the photographer used a"paintbrush of light."
Palette
See"Color Palette."
Pancake Lens
A thin, flat lens with a very short lens barrel often used for traveling because it is so compact.
Panning
Taking a picture with a relatively slow shutter speed and then tracking the motion of a subject such as horse so that the background is blurry but the horse is still sharp and in focus.
Panorama
Capturing a series of images to create a picture wider than what you could capture in a single image, by"stitching" the photographs together. Stitching is performed in a variety of image-editing software such as Photoshop.
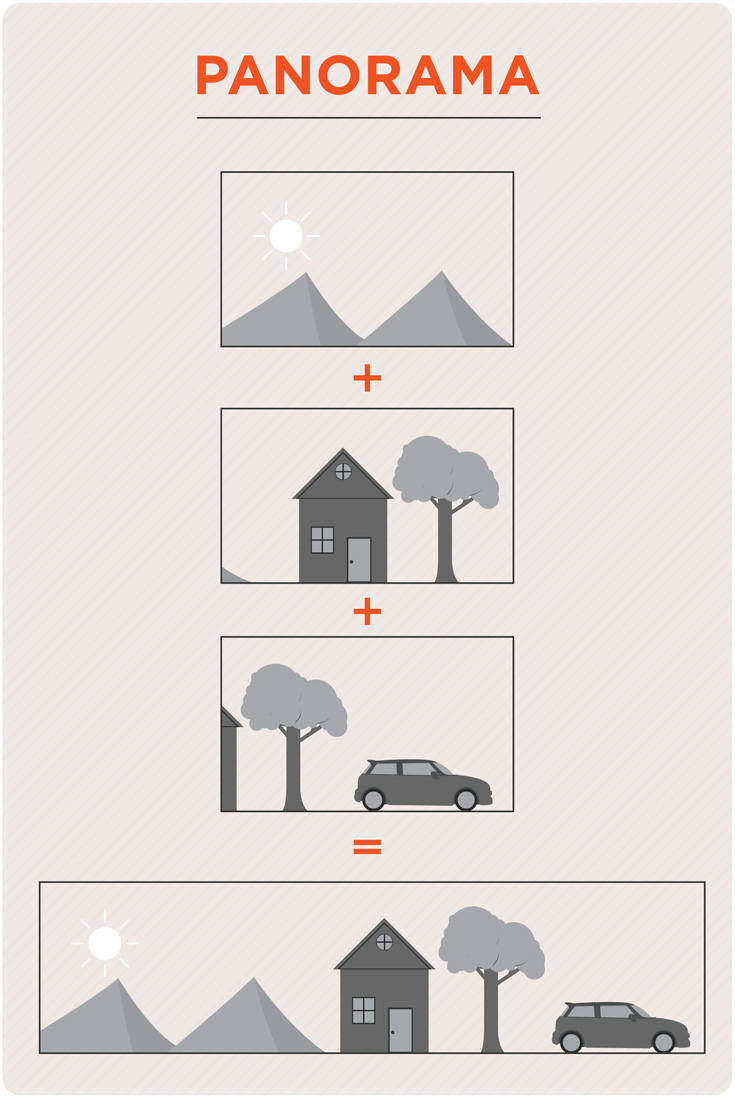
Paparazzi
Photographer who shoots candid, surreptitious or surprise shots, but not posed pictures, of celebrities and their families, often for publication in tabloids and magazines.
Parallax
The difference between the image seen by a viewing system and the image recorded by the imaging sensor. In point-and-shoot cameras, as subjects move closer to the lens, the variance increases. Only through-the-lens (TTL) viewing systems avoid parallax error.
PC
Denotes a type of flash synch connector, popular on most film and high-end digital cameras.
PC Card
PCMCIA cards are about the size of a credit card and a less common way to transfer files from a camera to a computer.
PC Sync
A standardized connector to connect and synchronize external electronic flash units (strobes) to cameras.
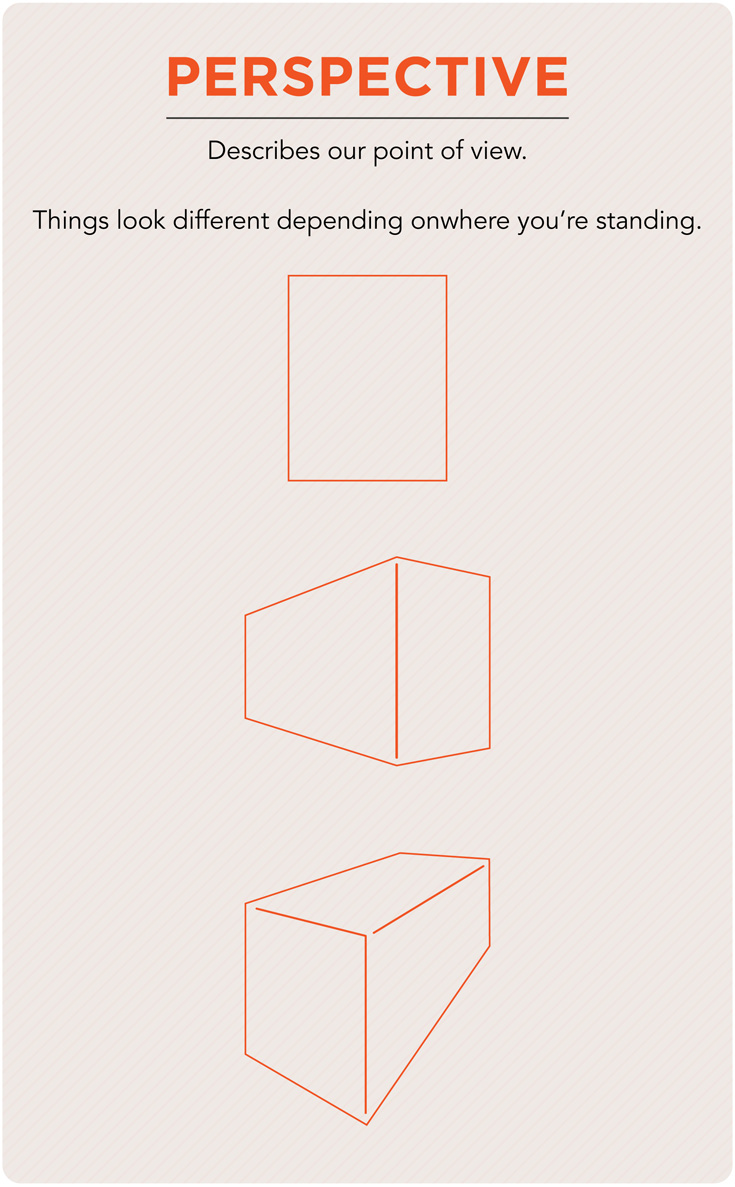
Perspective
Perspective is an element of photography determined by the angle of view from which the image is captured.
Photo
Greek term for"light," used to describe a single image.
Photo Slave
A flash unit that will fire simultaneously with another flash unit when the light sensitive feature is triggered.
Photobomb
A photograph that has been spoiled by the unexpected appearance of an unintended subject in the camera’s field of view as the picture was taken.
Photoshop
A software program created by Adobe to digitally edit photographic images.
PICT
File format designed to support RGB color spaces with a dominant single alpha channel. It is especially effective when compressing images of a single color.
PictBridge
Involves direct USB printing from digital cameras to printers and does not require the use of a computer.
PIM (Print Image Matching)
A standard for embedded color and printing information for digital cameras, developed by Epson. Camera manufacturers embed PIM information in the Exif header of JPEGs.
Pin-Cushioning
Common in less expensive lenses, when parallel lines on the horizontal or vertical plane bow inward. The opposite of barrel distortion.
Pixel
Stands for picture element, and refers to the smallest component within a digital image. Pixels are also the individual components that collectively recreate the image captured with your digital camera on a computer monitor. The more pixels there are, the higher the screen or image resolution will be.
![]()
Pixel peeper
Someone who spends too much time looking at images files fully zoomed in on their computer and reads noise and resolution ’at the pixel level’ rather than looking at the picture as a whole.
Pixelization
The breakup of a low-resolution digital image caused by having too few pixels. The pixels within a photograph become more noticeable and can no longer blend together to form a smooth image.
Plug-n-Play
An installation process used to connect to Microsoft Windows. New devices that are plugged into the computer are automatically recognized and the user is prompted with a variety of options.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
A patent-free alternative to GIF, this format is normally used for displaying images on the web and is considered to be lossless.
Point and Shoot
Automatic cameras that simplify taking pictures by only requiring the user to press the shutter button.

Polarized Light
Light that is reflected or transmitted through certain media so that all vibrations are restricted to a single plane.
Polarizing Filter
An adjustable filter, with two rings that change the filter’s effectiveness. The outer ring absorbs glare and darkens blue skies when rotated appropriately.
Portrait
A picture of a person that captures their likeness.
Pose
The assumed position of the subject in relation to the camera. Pose includes variations in posture and placement of head, hands, feet, etc.
PPI (Pixels Per Inch)
A measure of resolution in relation to an image. See"DPI."

Pre-Flash
A low-power flash that emits light before the main flash to automatically set the exposure and white balance.
Preview Button
A preview button that brings the lens down to the aperture selected by the photographer, allowing them to see which areas of the foreground or background are in focus.
Prime
A fixed focal length lens that remains constant with no ability to zoom. Prime lenses are often of higher optical quality because they have a wider minimum aperture.
A photographic image printed on paper either from a digital file or a negative.
Programmed AE
A mode in which the camera chooses the best shutter speed and aperture automatically.
Proof
A sample image intended for the purpose of ensuring that the monitor and printer are calibrated correctly. If a digital image includes a watermark it may be also considered to be a proof.
PSD (Photoshop Document)
An image file type created in Adobe PhotoShop. A PSD file lets the user save a picture they are working on with all of the image-editing data intact.
Q
QVGA
Quarter VGA resolution (320 x 240) for motion video.
R
Racking Focus
Used to direct the attention of a viewer by rotating the focus of the lens from the foreground to the background or vice versa.
Rangefinder
The viewfinder on most small cameraas that is a separate viewing device and independent of the lens. It can be found on Diana cameras and Polaroids and is often above the lens or to the left or right.
RAW
Unedited version of an image specific to the photographer’s camera settings. RAW files have a much more robust editing ability and hold more information than many of the other standard file formats.
Red-Eye
An image in which a subjects has red irises. This happens when the interior back of the eye is illuminated from a flash and has light travel through it.
Red-Eye Reduction
A method of reducing or eliminating red-eye from flash photographs by using a pre-flash prior to taking the picture.
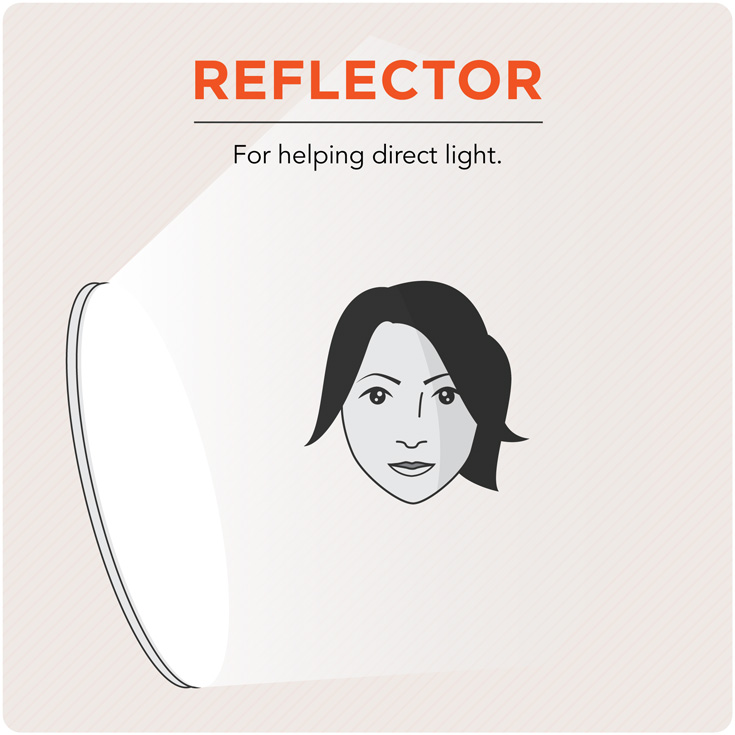
Reflector
A specific type of shiny or white material used to reflect light in a specific direction.
Reflex Camera
A camera that utilizes a mirror system to reflect light into a visible screen. The scene in the camera’s viewfinder is the same image that is being seen through the lens.
Resampling
Occurs when an image editing program is used to change an image’s size. Increasing an image’s size requires the addition of new pixels and decreasing size removes pixels.
Resin Coated Paper
Paper that has a water repellent base and is used for making photographic prints.
Model release
A contract in which a model consents to the use of his or her images by the photographer or a third party.
Rembrandt Lighting
A lighting technique used in studio portrait photography that requires minimal use of lighting equipment but gives a natural and compelling look to the subject.
Remote Capture
The ability to signal the camera shutter to fire from a distance using a cable release or wireless transmitter.
Render
The final step of an image transformation when a new image has been refreshed on a computer screen.
Resize
To take an image and adjust the size specifications, often when preparing it for print. Most editing programs offer a resize option labeled as"cropping."
Resolution
The number of pixels used to capture or display an image. The higher the resolution is the more detail an image will have.
Retouching
To improve an image’s appearance by physically or digitally altering a print or image file.
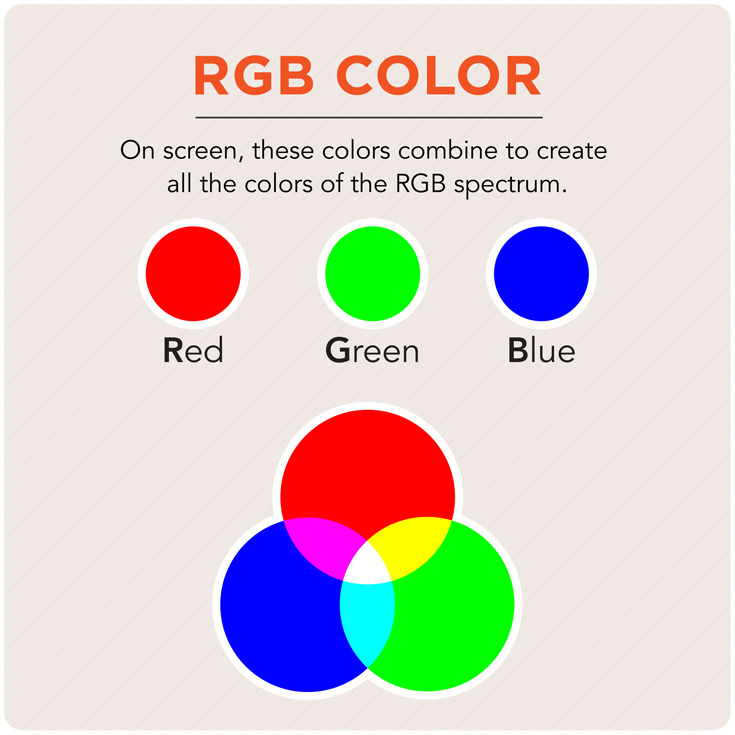
RGB Color (Red Green Blue)
A color space comprised of 256 variations of color that is used in digital cameras and image editing software.
Rig
A support system to maintain focus and avoid camera shake while in motion. Often worn to get a smooth look when using a digital camera for video recording purposes.
Rim Lighting
When the key light is behind the subject so that the subject’s face is located completely in shadow. The subject also has a rim of light emphasizing the contour of their head.
Ring Flash
A circular-shaped electronic flash fitted around a lens that is used in close-up photography because the subject is often shadowless and maintains uniform frontal lighting.
Rule of Thirds
A design principle made up of a grid that breaks up the composition of an image into 9 separate squares suggesting that the photogapher place the subject at one of intersecting lines.

S
Safelight
A lamp is used in a darkroom to view light-sensitive material in dim conditions without ruining the exposure of the print.
Saturation
The depth of the color within an image. The deeper the level of color the more saturated a photo is, while less saturation gives a more muted look to the color palette.
Scale
Describes the size of a subject relative to its surroundings or immediate environment.
Scanner
Scans and converts photographs from a tangible image into a digital file that can be manipulated and saved on a computer.
Scene Modes
An exposure mode that allows the photographer to select a pre-programmed scene from a list of options given in the menu of a digital camera. This mode is very prevalent in point and shoot cameras.
SD Card (Secure Digital)
A reduced size of the compact flash memory card that is often found in cell phones and modern digital cameras.
Selective Focus
A tool employed using shallow depth of field, so that the subject is isolated from its surroundings because the surroundings are not in focus.
Selfie
A photographic self portrait usually taken at arm’s length, or one’s own reflection photographed in a mirror. This style of photography is amatuer and is very prevalent in contemporary society due to the technology associated with camera phones.
Self Timer
A preset time delay (ie. 2 or 10 seconds) before the shutter fires automatically. Photographers use this technique to avoid camera shake as well as put themselves in a photograph when using a tripod.

Sepia
A brownish effect seen in photos from the 19th century that is now an option in image editing software.
Shadow
The darkest part of the scene within an image, predominantly a range of black tonal values.
Shadow Detail
The detail that is visible within the darkest parts of an image.
Sharpness
An image’s degree of clarity in terms of focus and contrast.
Sheet Film
A piece of film sized for one exposure in a view camera.
Shift Lens
A lens that allows the photographer to control the appearance of perspective by adjusting the lens’ relationship to the image sensor. This type of lens gives effects similar to a view camera.
Shutter
A mechanism in the camera that controls the amount of light that reaches the film or sensor.
Shutter Count
The number of pictures or"actuations" a camera has taken. Professional cameras are rated for 200,000 actuations with a single shutter.
Shutter Lag
The time between when the shutter is pressed and when the image is captured. Point and Shoot cameras have a longer shutter lag time because it must calculate exposure before taking the picture.
Shutter Priority
A metering mode where shutter speed is chosen and fixed allowing the camera to choose the appropriate aperture setting. Usually denoted with an S.
Shutter speed
The length of time the shutter remains open after the shutter release has been pressed, usually measured in fractions of second.
Silhouette
A dark image outlined against a lighter background. This occurs when the photographer is capturing an image with the light source facing them.
Skylight Filter
A filter that absorbs UV Light and reduces the abundance of blue in an image.
Slow Sync
A flash mode in some digital cameras that opens the shutter for a longer period of time than normal. This technique is used for proper illumination of both the background and foreground.
SLR (Single Lens Reflex)
A camera utilizing a prism and mirror system to project the image seen by the lens onto a focusing screen. The image is then seen through the viewfinder exactly as it is seen through the lens.
SmartMedia
A flash memory card that consists of a thin piece of plastic with laminated memory on the surface and a gold contact strip to connect to the camera. SmartMedia cards are available in various sizes.
Snapshot
An informal photograph taken quickly by a hand-held camera.
Soft Focus
A soft look achieved bending light and dispersing highlights so that the image still remains in focus but gives the subjet a soft look.
Softbox
A type of photographic lighting device that creates soft or"flat" lighting. All the various soft light types create even and diffused light by directing light through some diffusing material.

Spot Metering
A type of metering that involves reading the reflected light off the subject of the photograph, rather than pointing the light meter directly at the light source. This measures only a very small part of the scene.
sRGB
The standard color space for the internet. It provides a smaller range of colors than the RGB color space.
Stitching
Combining a series of images to form a larger image or a panoramic photo. This requires the use of image editing software.
Stock Photography
Photographs that are supplied through licensing and intended for specific use. Stock photos can be found in mass amounts on various websites such as Getty Images.
Stop
A form of measurement when referring to aperture. Stops in order - 1.8, 2, 2.8, 4, 5.6, 8, 11, 16, 22, 32, 64.
Stopping Down
Stopping down indicates that the photographer is increasing the f-stop number, therefore decreasing the size of the aperture and making the image sharper.
Storage Card (Memory Card)
A memory storage device for digital cameras.
Street Photography
A form of photography that features humans within public places.
Studio
A room specially equipped for photography, often with a blank backdrop and a variety of lighting equipment.
SVGA (Super VGA)
Refers to an image resolution size of 800 x 600 pixels.
Synch Cord
An electrical cord connecting a camera to an electronic flash that is used to permit synchronized flash.
T
T (Time)
A shutter speed mode used for extended time exposures. The shutter opens when the release is pressed and closes when it is pressed again.
Tele-Converter
A lens mounted between a camera body and a lens that is used to increase the focal length of the lens. A 100mm lens becomes 140mm when a 1.4x extender is placed between it and the camera body.
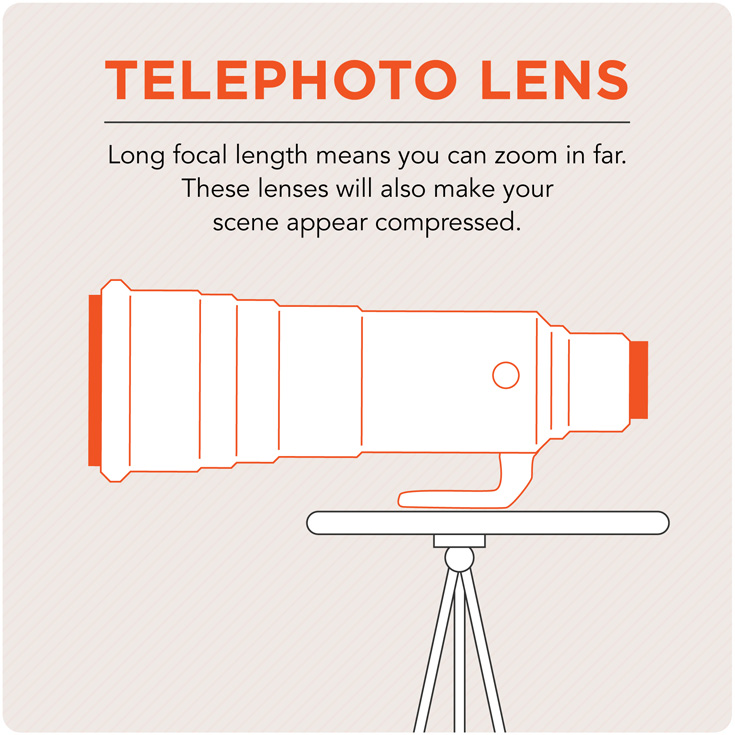
Telephoto Lens
A lens with a long focal length and narrow angle of view that exhibits shallow depth of field through its magnification of focal length.
Test Shots
A series of images photographed at the beginning of a shoot, often with a stand-in rather than the actual model. These images are taken to allow the photographer to determine proper exposure, depth of field and lighting for a photo shoot.
Texture
The visual quality of the surface of an object revealed through variances in shape, tone and color depth. Lighting has the most influence over how texture will look in an image.
TFT
A high resolution color LCD screen used in digital cameras.
Thumbnail
Small images that appear in an image browser or on the LCD of a digital camera.
TIFF (Tagged-Image File Format)
A bitmap image file supported by virtually all image software applications. This is a"lossless" file and maintains detail and resolution of a photo even during compression.
Time Lapse
Photographs captured over time intervals such as seconds, minutes, days, weeks or years.
Tonal Range
The quality of color and tone within an image ranging from the darkest to brightest area and everything in between.
Tone
The degree of lightness, darkness, or color variation in an image. Can also be known as"value."
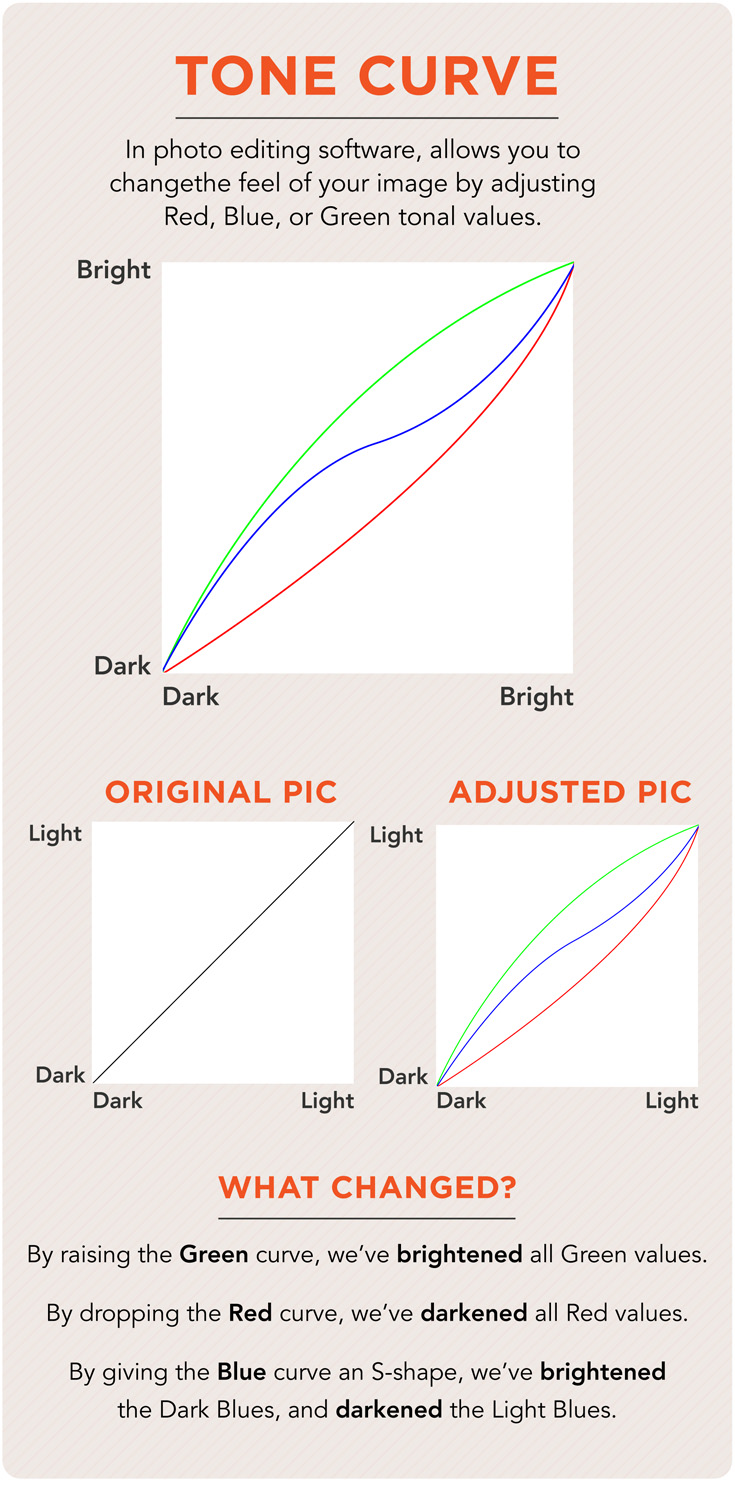
Tone Curve
A graph used in image editing software to display the value within the photo. The tone curve is adjustable in terms of both light and color.
Tran reflective
A type of LCD display that uses both ambient light and a backlight to illuminate the pixels of the screen which makes it easier to see in brighter conditions.
Tripod
A pole that has a base of three legs that provides support to a camera when filming or taking photos in low light. This prevents camera shake and allows photographers to take long exposures, eg: night photography.
True Color
Color in a digital image that has a depth of 24-bits per pixel and a total of 16.7 million colors.
TTL (Through the Lens)
A metering system that determines the proper exposure based on a reading through the lens and onto the image sensor. These are the most accurate of exposure readings and normally filter out any peculiarities.
Tungsten Light
Refers to artificial room lighting, normally at a color temperature of 3200 K.
U
Umbrella
A lighting accessory that resembles a rain umbrella, used to soften illumination by bouncing or diffusing the light.

Uncle Bob
The name that wedding photographers give to a wedding guest who comes armed with a big DSLR and accessories. Uncle Bob can often be found in the photographer’s way or in the photograph unnecessarily.
Underexposure
When too little light is recorded while taking a picture, which can result in a dark image. Underexposure can be corrected digitally, but noise may be present when attempting to bring detail out of the darker areas of the image.
Unsharp Masking
When detail and sharpness of an image is increased via image editing software.
Upload
To transfer information from one device to another. Photographers often upload their images from camera to computer, and then subsequently upload the images from the computer to a hard drive for storage.
USB
The data I/O port on most digital cameras that is also found on most modern computers.
UXGA
Refers to an image resolution size of 1600 x 1200 pixels.
V
VGA
Refers to an image resolution size of 640 x 480 pixels.
View Camera
A large format camera that produces an individual image size of 5" X 4" or larger.
Video Mode
The ability of a digital camera to capture video by keeping the shutter open rather than opening and closing when capturing an image.
Video Out
Some digital cameras have the ability to output images on television screens and computer monitors by connecting them with a cord and using either NTSC or PAL format.
Viewfinder
The area used for composing and focusing the subject being photographed and viewing the entire frame of the image. Viewfinders can be glass (Rangefinder) or an LCD screen that views the live image.
Vignetting
Darkening of the edges of a photographic image evenly to direct the view towards the center of an image.

W
Watermark
The information that is embedded in the image data to protect the copyrights of the image.
White Balance
The camera’s ability to correct color in any given situation given the source of ambient or artificial light.
Wide-Angle Lens
A lens with an angle of view that is wider than that of a normal lens, or that of the human eye. A wide-angle lens has a focal length shorter than the focal length of a normal lens and sometimes has distoration at the end of the image. Standard-wide angle lenses are 28-35mm while super-wide is anything wider than 28mm.
X
XGA
Refers to an image resolution size of 1024 x 768 pixels.
Y
Yellow Filter
The most-popular colored filter used with black and white film. Because a yellow filter absorbs blue, it provides significantly greater contrast between blue and yellow or white subjects.
Z
Zoom
The action of varying the focal length of a zoom lens to enlarge (zoom in) or reduce (zoom out) the image.
Zoom creep
A lens’ tendency to extend or shorten the focal length without the photographer’s intent. This is due to an upward or downward tilt of the lens.





